Persistence ACL feature configuration
Edit on GitHubThis document describes how you can configure the Persistence ACL feature.
The Persistence ACL functionality is based on the Propel behavior. You can enable the feature in two different ways:
Connect Persistence ACL feature to one or more database tables
In the following code snippet, only the SpyMerchant entity is configured to be handled by ACL.
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<database xmlns="spryker:schema-01"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
name="zed"
xsi:schemaLocation="spryker:schema-01 https://static.spryker.com/schema-01.xsd"
namespace="Orm\Zed\Merchant\Persistence"
package="src.Orm.Zed.Merchant.Persistence">
<table name="spy_merchant">
<behavior name="\Spryker\Zed\AclEntity\Persistence\Propel\Behavior\AclEntityBehavior"/>
</table>
</database>
Connect Persistence ACL feature to all database tables
ACL handles all entities in the system in the following example. When configuring ACLs in such a way, be sure to use the Allowed entity list to exclude entities that are needed to function properly. Provide the list of entities that are needed:
SpyUserSpyAclRoleSpyAclGroupSpyAclRuleSpyAclEntityRuleSpyUrlSpyAclEntitySegmentSpyAclGroupsHasRolesSpyAclUserHasGroup
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<database xmlns="spryker:schema-01"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
name="zed"
xsi:schemaLocation="spryker:schema-01 https://static.spryker.com/schema-01.xsd"
namespace="Orm\Zed\AclEntity\Persistence"
package="src.Orm.Zed.AclEntity.Persistence">
<behavior name="\Spryker\Zed\AclEntity\Persistence\Propel\Behavior\AclEntityBehavior"/>
</database>
Persistence ACL feature configuration
The configuration, unlike the rule, is common to the entire system. The main configuration object for the feature is \Generated\Shared\Transfer\AclEntityMetadataConfigTransfer. Through the plugin system, it can be extended. You just need to create a plugin and implement \Spryker\Zed\AclEntityExtension\Dependency\Plugin\AclEntityMetadataConfigExpanderPluginInterface.
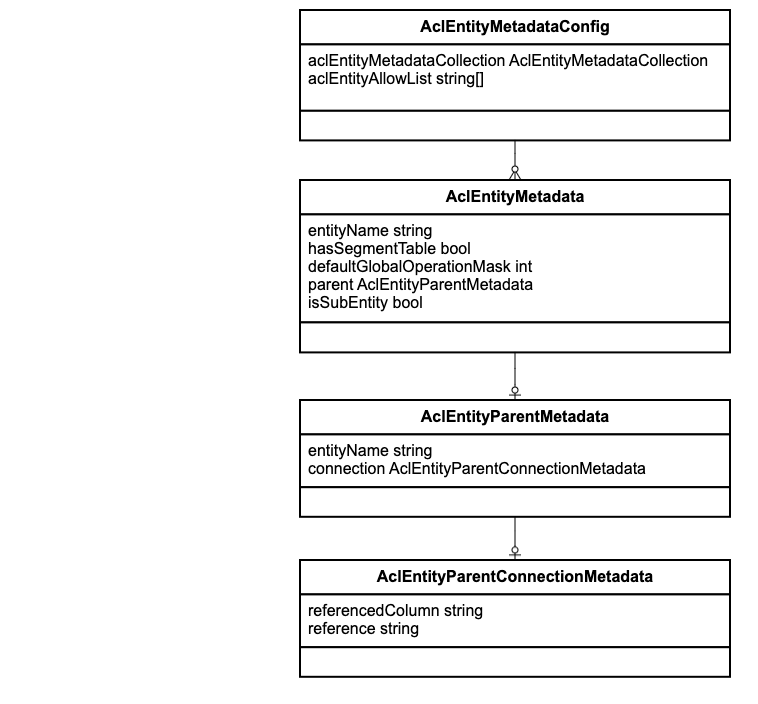
AclEntityMetadataConfigTransfer
The properties of the AclEntityMetadataConfigTransfer are described in the following table.
| PROPERTY | TYPE | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|---|
| aclEntityMetadataCollection | AclEntityMetadataCollectionTransfer | The collection of configurations for different entities. |
| aclEntityAllowList | string[] | The set of fully qualified classes that this feature does not apply to (even if the user has rules for an entity that is in the allowlist). |
AclEntityMetadataCollectionTransfer
The properties of the AclEntityMetadataCollectionTransfer are described in the following table.
| PROPERTY | TYPE | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|---|
| collection | AclEntityMetadataTransfer[] | The set of configurations for the models. |
AclEntityMetadataTransfer
The properties of the AclEntityMetadataTransfer are described in the following table.
| PROPERTY | TYPE | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|---|
| parent | AclEntityParentMetadataTransfer | This property is used to configure the inheritance. It is required for the entity which has rules with the inherited scope, or for the composite entity. For more details, see Inherited scope vs Composite entity. |
| entityName | string | Fully qualified class name of the configured entity (Propel Entity). |
| hasSegmentTable | bool | Sets if the configured entity supports segmentation. For more details, see Segment scope documentation. |
| defaultGlobalOperationMask | int | Sets the default binary access mask (see Execution flow documentation). |
| isSubentity | bool | Indicates whether the configured entity is the part of a composite object. For more details, see Composite entity. |
AclEntityParentMetadataTransfer
The properties of the AclEntityParentMetadataTransfer are described in the following table.
| PROPERTY | TYPE | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|---|
| connection | \Generated\Shared\Transfer\AclEntityParentConnectionMetadata | This property is used to set up the relationship between the current class and the parent. |
| entityName | string | Fully qualified class name of the parent entity. |
AclEntityParentConnectionMetadataTransfer
The properties of the AclEntityParentConnectionMetadataTransfer are described in the following table.
Sometimes, foreign keys are not used to link the child and parent tables, but rather “reference columns”. As a result, a AclEntityParentConnectionMetadataTransfer is available.
| PROPERTY | TYPE | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|---|
| reference | string | Current class field. |
| referencedColumn | string | Parent class field. |
Examples of configuration
This section provides examples of ACL configuration.
Basic inheritance configuration
This section shows how you can inherit the SpyProduct from SpyStore by using the SpyProductAbstract and the SpyProductAbstractStore.
This configuration is necessary to use the functionality of the Inherited scope rules and Composite entity.
/**
* @param \Generated\Shared\Transfer\AclEntityMetadataConfigTransfer $aclEntityMetadataConfigTransfer
*
* @return \Generated\Shared\Transfer\AclEntityMetadataConfigTransfer
*/
public function expand(AclEntityMetadataConfigTransfer $aclEntityMetadataConfigTransfer): AclEntityMetadataConfigTransfer
{
$aclEntityMetadataConfigTransfer->getAclEntityMetadataCollectionOrFail()->addAclEntityMetadata(
SpyProduct::class,
(new AclEntityMetadataTransfer())
->setEntityName(SpyProduct::class)
->setParent(
(new AclEntityParentMetadataTransfer())
->setEntityName(SpyProductAbstract::class)
)
);
$aclEntityMetadataConfigTransfer->getAclEntityMetadataCollectionOrFail()->addAclEntityMetadata(
SpyProductAbstract::class,
(new AclEntityMetadataTransfer())
->setEntityName(SpyProductAbstract::class)
->setParent(
(new AclEntityParentMetadataTransfer())
->setEntityName(SpyProductAbstractStore::class)
)
);
$aclEntityMetadataConfigTransfer->getAclEntityMetadataCollectionOrFail()->addAclEntityMetadata(
SpyProductAbstractStore::class,
(new AclEntityMetadataTransfer())
->setEntityName(SpyProductAbstractStore::class)
->setParent(
(new AclEntityParentMetadataTransfer())
->setEntityName(SpyStore::class)
)
);
$aclEntityMetadataConfigTransfer->getAclEntityMetadataCollectionOrFail()->addAclEntityMetadata(
SpyStore::class,
(new AclEntityMetadataTransfer())
->setEntityName(SpyStore::class)
);
return $aclEntityMetadataConfigTransfer;
}
The inheritance through the reference column
In some databases, data is linked not by foreign keys but by “reference columns”.
Below is an example of inheriting SpyAvailability from SpyProduct through a reference column (sku in this example).
Pay attention to the AclEntityParentConnectionMetadataTransfer property.
/**
* @param \Generated\Shared\Transfer\AclEntityMetadataConfigTransfer $aclEntityMetadataConfigTransfer
*
* @return \Generated\Shared\Transfer\AclEntityMetadataConfigTransfer
*/
public function expand(AclEntityMetadataConfigTransfer $aclEntityMetadataConfigTransfer): AclEntityMetadataConfigTransfer
{
$aclEntityMetadataConfigTransfer->getAclEntityMetadataCollectionOrFail()->addAclEntityMetadata(
SpyAvailability::class,
(new AclEntityMetadataTransfer())
->setEntityName(SpyAvailability::class)
->setParent(
(new AclEntityParentMetadataTransfer())
->setEntityName(SpyProduct::class)
->setConnection(
(new AclEntityParentConnectionMetadataTransfer())
->setReference('sku')
->setReferencedColumn('sku')
)
)
);
$aclEntityMetadataConfigTransfer->getAclEntityMetadataCollectionOrFail()->addAclEntityMetadata(
SpyProduct::class,
(new AclEntityMetadataTransfer())->setEntityName(SpyProduct::class)
);
return $aclEntityMetadataConfigTransfer;
}
Composite entity
Below you can find an example of a Composite entity SpyMerchant, which consists of:
SpyMerchantSpyMerchantProfileSpyMerchantUserSpyMerchantStore
/**
* @param \Generated\Shared\Transfer\AclEntityMetadataConfigTransfer $aclEntityMetadataConfigTransfer
*
* @return \Generated\Shared\Transfer\AclEntityMetadataConfigTransfer
*/
public function expand(AclEntityMetadataConfigTransfer $aclEntityMetadataConfigTransfer): AclEntityMetadataConfigTransfer
{
$aclEntityMetadataConfigTransfer->getAclEntityMetadataCollectionOrFail()->addAclEntityMetadata(
SpyMerchantProfile::class,
(new AclEntityMetadataTransfer())
->setEntityName(SpyMerchantProfile::class)
->setIsSubEntity(true)
->setParent(
(new AclEntityParentMetadataTransfer())
->setEntityName(SpyMerchant::class)
)
);
$aclEntityMetadataConfigTransfer->getAclEntityMetadataCollectionOrFail()->addAclEntityMetadata(
SpyMerchantUser::class,
(new AclEntityMetadataTransfer())
->setEntityName(SpyMerchantUser::class)
->setIsSubEntity(true)
->setParent(
(new AclEntityParentMetadataTransfer())
->setEntityName(SpyMerchant::class)
)
);
$aclEntityMetadataConfigTransfer->getAclEntityMetadataCollectionOrFail()->addAclEntityMetadata(
SpyMerchantStore::class,
(new AclEntityMetadataTransfer())
->setEntityName(SpyMerchantStore::class)
->setIsSubEntity(true)
->setParent(
(new AclEntityParentMetadataTransfer())
->setEntityName(SpyMerchant::class)
)
);
$aclEntityMetadataConfigTransfer->getAclEntityMetadataCollectionOrFail()->addAclEntityMetadata(
SpyMerchant::class,
(new AclEntityMetadataTransfer())->setEntityName(SpyMerchant::class)
);
return $aclEntityMetadataConfigTransfer;
}
Data segmentation support
The following is an example of the data segmentation for the SpyMerchant. Data segmentation is required for the Segment scope rules.
/**
* @param \Generated\Shared\Transfer\AclEntityMetadataConfigTransfer $aclEntityMetadataConfigTransfer
*
* @return \Generated\Shared\Transfer\AclEntityMetadataConfigTransfer
*/
public function expand(AclEntityMetadataConfigTransfer $aclEntityMetadataConfigTransfer): AclEntityMetadataConfigTransfer
{
$aclEntityMetadataConfigTransfer->getAclEntityMetadataCollectionOrFail()->addAclEntityMetadata(
SpyMerchant::class,
(new AclEntityMetadataTransfer())
->setEntityName(SpyMerchant::class)
->setHasSegmentTable(true)
);
return $aclEntityMetadataConfigTransfer;
}
Default operation mask
The following example sets the default Read permissions for the SpyCountry and Create + Read permissions for the SpyResetPassword.
/**
* @param \Generated\Shared\Transfer\AclEntityMetadataConfigTransfer $aclEntityMetadataConfigTransfer
*
* @return \Generated\Shared\Transfer\AclEntityMetadataConfigTransfer
*/
public function expand(AclEntityMetadataConfigTransfer $aclEntityMetadataConfigTransfer): AclEntityMetadataConfigTransfer
{
$aclEntityMetadataConfigTransfer->getAclEntityMetadataCollectionOrFail()->addAclEntityMetadata(
SpyCountry::class,
(new AclEntityMetadataTransfer())
->setEntityName(SpyCountry::class)
->setDefaultGlobalOperationMask(AclEntityConstants::OPERATION_MASK_READ)
);
$aclEntityMetadataConfigTransfer->getAclEntityMetadataCollectionOrFail()->addAclEntityMetadata(
SpyResetPassword::class,
(new AclEntityMetadataTransfer())
->setEntityName(SpyResetPassword::class)
->setDefaultGlobalOperationMask(
AclEntityConstants::OPERATION_MASK_CREATE | AclEntityConstants::OPERATION_MASK_READ
)
);
return $aclEntityMetadataConfigTransfer;
}
Allowlist configuration
The following example adds all the entities required for the Persistence Acl to function correctly:
/**
* @param \Generated\Shared\Transfer\AclEntityMetadataConfigTransfer $aclEntityMetadataConfigTransfer
*
* @return \Generated\Shared\Transfer\AclEntityMetadataConfigTransfer
*/
public function expand(AclEntityMetadataConfigTransfer $aclEntityMetadataConfigTransfer): AclEntityMetadataConfigTransfer
{
$aclEntityMetadataConfigTransfer
->addAclEntityAllowListItem(SpyUser::class)
->addAclEntityAllowListItem(SpyAclRole::class)
->addAclEntityAllowListItem(SpyAclGroup::class)
->addAclEntityAllowListItem(SpyAclRule::class)
->addAclEntityAllowListItem(SpyAclEntityRule::class)
->addAclEntityAllowListItem(SpyUrl::class)
->addAclEntityAllowListItem(SpyAclEntitySegment::class)
->addAclEntityAllowListItem(SpyAclGroupsHasRoles::class)
->addAclEntityAllowListItem(SpyAclUserHasGroup::class);
return $aclEntityMetadataConfigTransfer;
}
Thank you!
For submitting the form
