Persistence ACL feature overview
Edit on GitHubWith the Persistence ACL feature, you can manage authorization at the database entity level, or even within a set of entities or segments. This feature enables a flexible system of inheritance of rights, simplifying the configuration of access.
Persistence ACL runs in the Persistence layer, as its name suggests.
Limitations
The module is based on the Propel ORM (namely Propel Behavior and Propel Hooks). If you are not using PropelOrm to interact with data in your system, this module will not work.
How it works
Persistence ACL supports permission checks both when executing queries and when performing actions on Active Record models. Upon installation and configuration, code is injected into the Active Record model and Query classes that check the user’s permissions for the appropriate actions. This module uses Propel hooks.
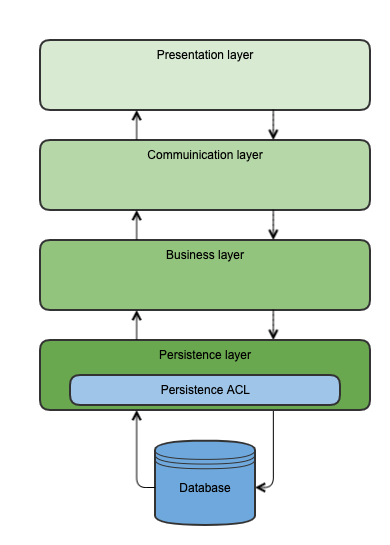
If you execute queries outside of Propel API, they WILL NOT be handled by Persistence ACL.
During model operations, the following hooks are used:
-
preInsert -
preUpdate -
preDelete
Query execution is performed using the following hooks:
-
preSelectQuery -
preUpdateQuery -
preDeleteQuery
A query sent to the database is intercepted and modified with additional joins to limit the results of the query to only those records available to the current user. If the user attempts to perform a restricted action on an Active Record model (such as updating, deleting, or creating), then \Spryker\Zed\AclEntity\Persistence\Exception\OperationNotAuthorizedException is thrown.
Learn more
Related Developer documents
| INSTALLATION GUIDES | REFERENCES | HOWTOS |
|---|---|---|
| Install the ACL feature | Persistence ACL feature configuration | HowTo: Split products by stores |
| Execution flow | ||
| Rules and scopes | ||
| Global scope | ||
| Segment scope | ||
| Inherited scope | ||
| Composite entity |
Thank you!
For submitting the form
