Self-Service Portal Service Management architecture overview
Edit on GitHubThis document provides an architecture overview of the Service Management feature, explaining how services are modeled, connected, and processed throughout the system.
Overview
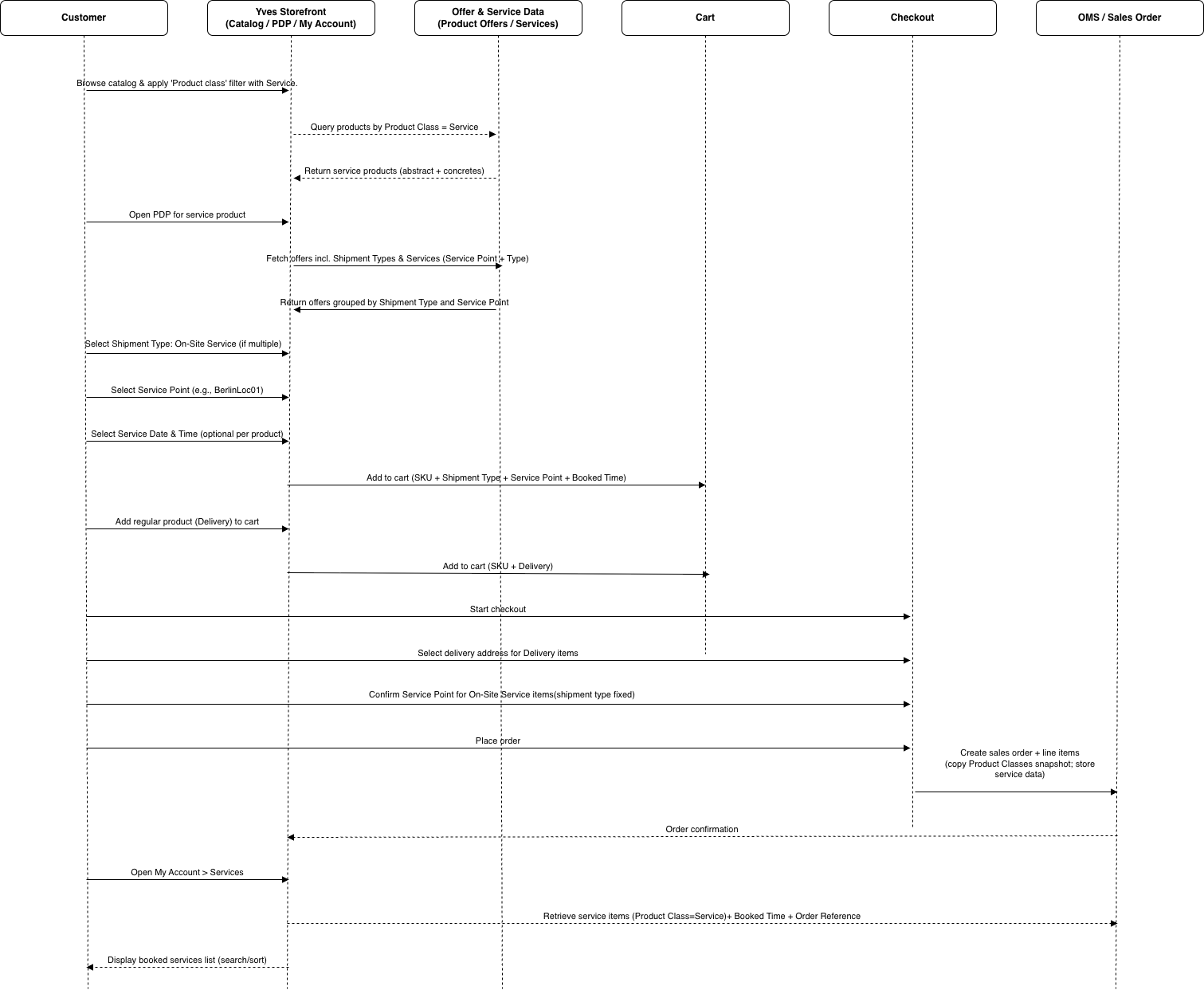
The Service Management feature lets you sell services through the catalog in the same way as products. Customers can book a service that is either delivered to their address or performed at a designated service point (for example, after-sales maintenance or repair). Each service offer defines where the service is provided (service point), what is provided (service type), and how it is fulfilled (shipment type such as On-Site Service or Delivery).
To sell services, you first prepare the operational setup. Service points must be imported with their addresses and enabled service types (for example, In-Center-Service). For each enabled combination, you then create a Service entity per service point (service point + service type), which represents the actual service availability at that location.
In parallel, shipment types must be imported (for example, Delivery and On-Site Service), and shipment methods must be imported and assigned to a specific shipment type so checkout can offer the correct fulfillment options.
Services are then modeled as service products by assigning a dedicated service product class, defining allowed shipment types per variant, and creating product offers that link the service product to the relevant service points, services ( service type + location), and shipment types. If scheduling is required, you can optionally enforce service date and time selection during checkout.
In marketplace scenarios, multiple merchants can publish offers for the same service product. On the Storefront, the product details page aggregates compatible offers, shows the available shipment types per offer, and filters offers based on the customer’s current asset or model context—enabling a unified self-service experience to compare and purchase compatible service options.
Storefront examples
Services can be found in the related category Services in the navigation bar.
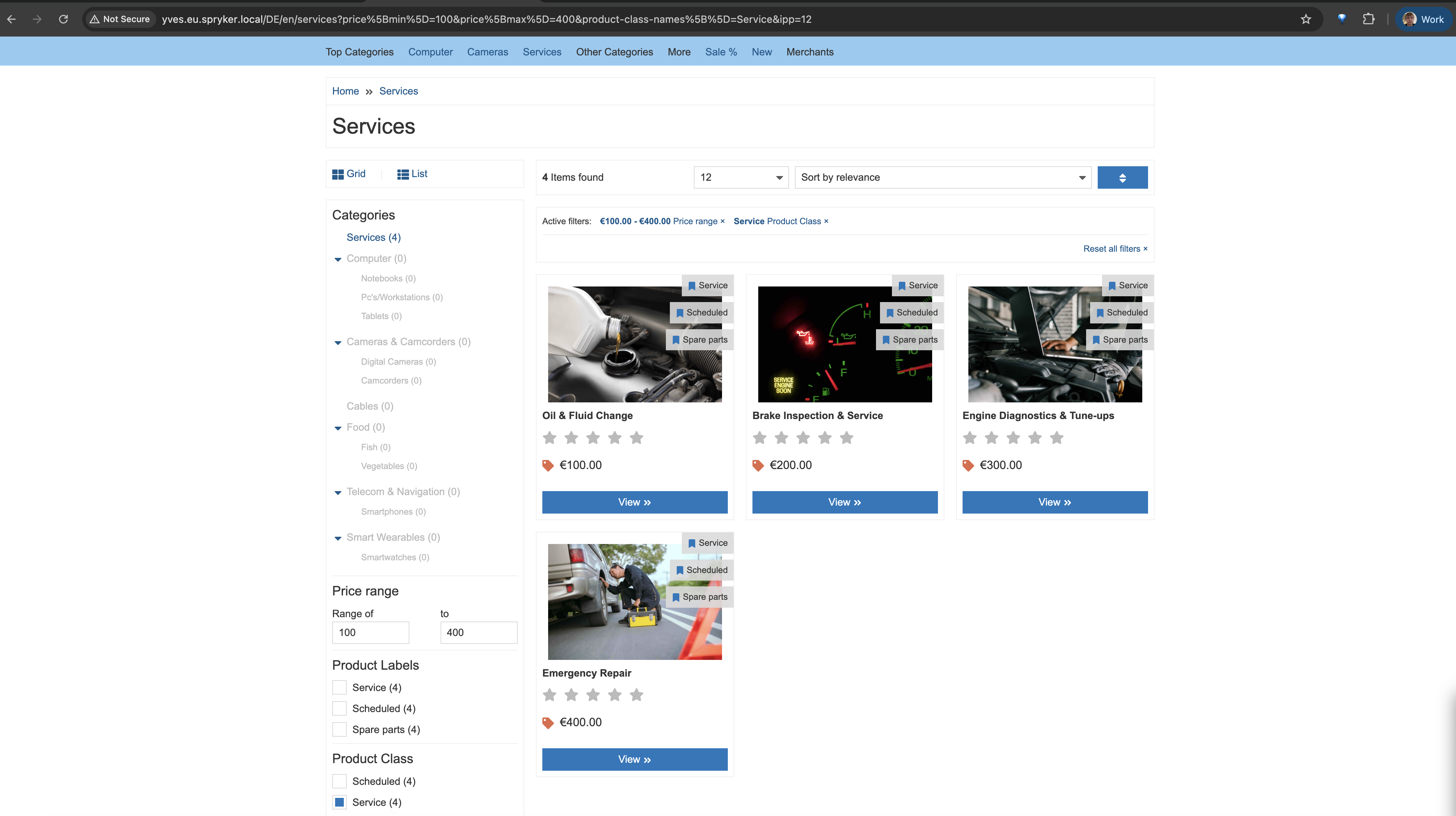
Below is an example of the service product PDP page, where customers can choose the shipment type and the most affordable option.
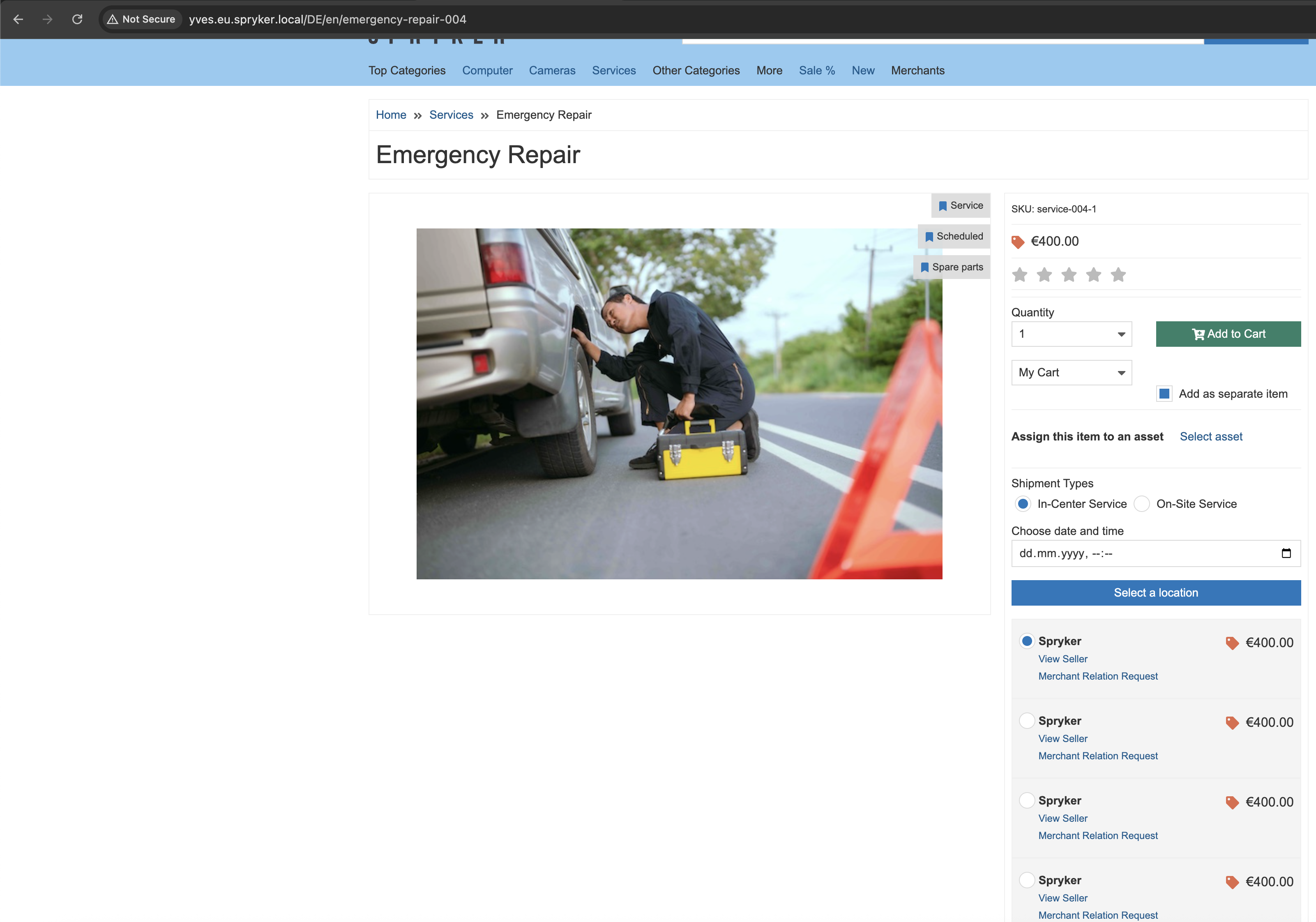
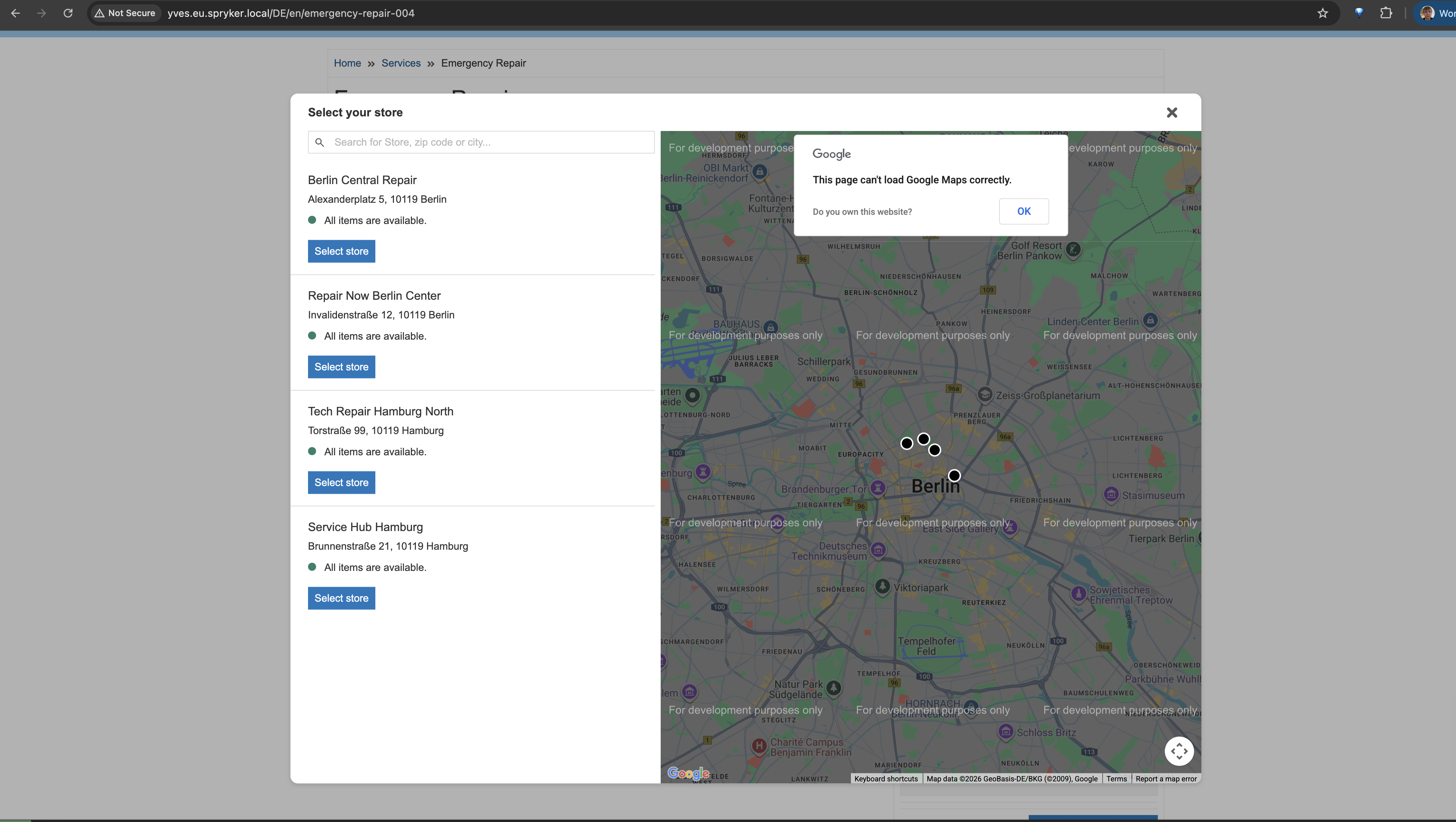
By pressing Select location, a modal window opens with the available offers at the service points.
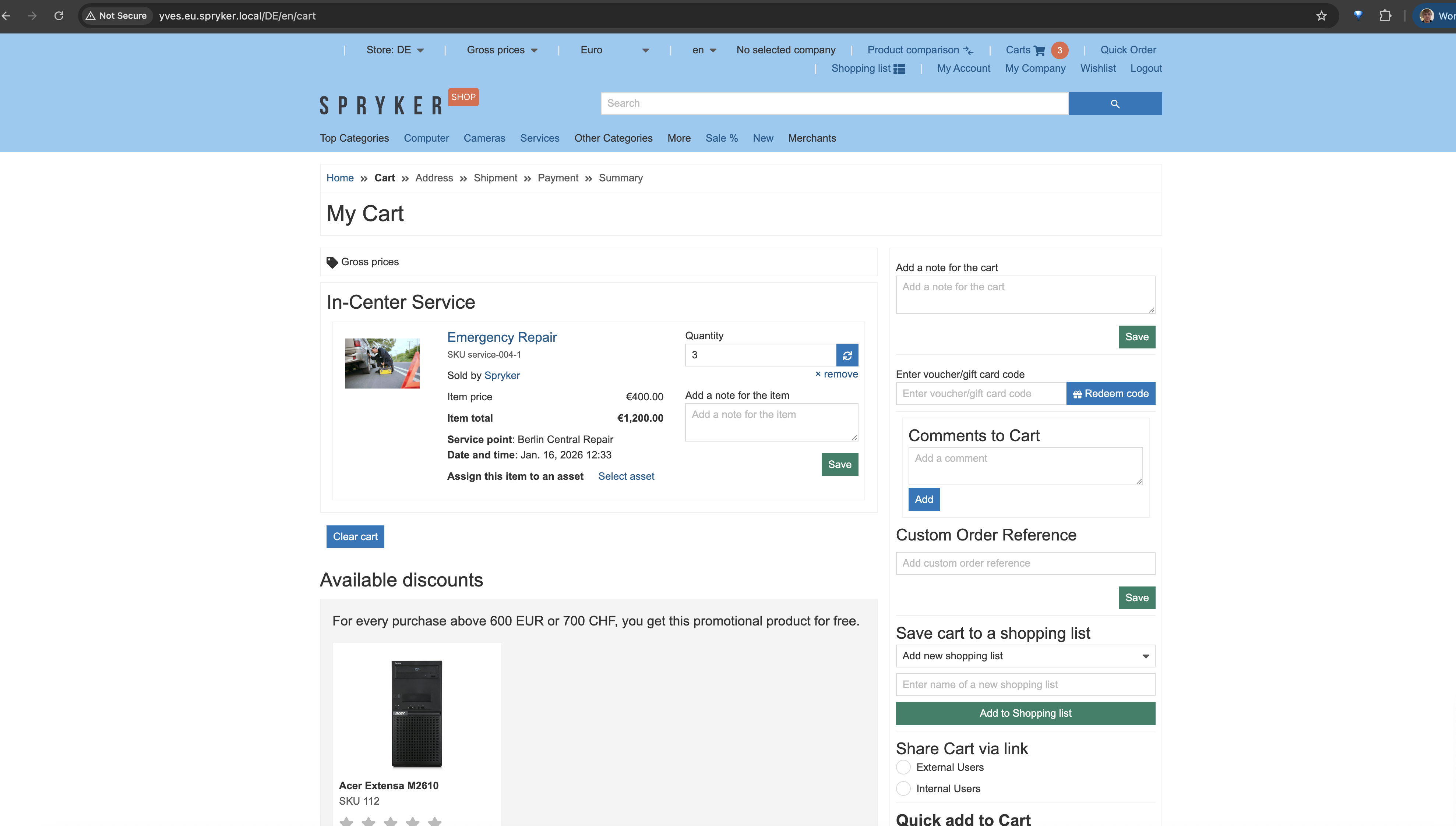
After adding the product to the cart, customers can check the location and preferred time to receive their service.
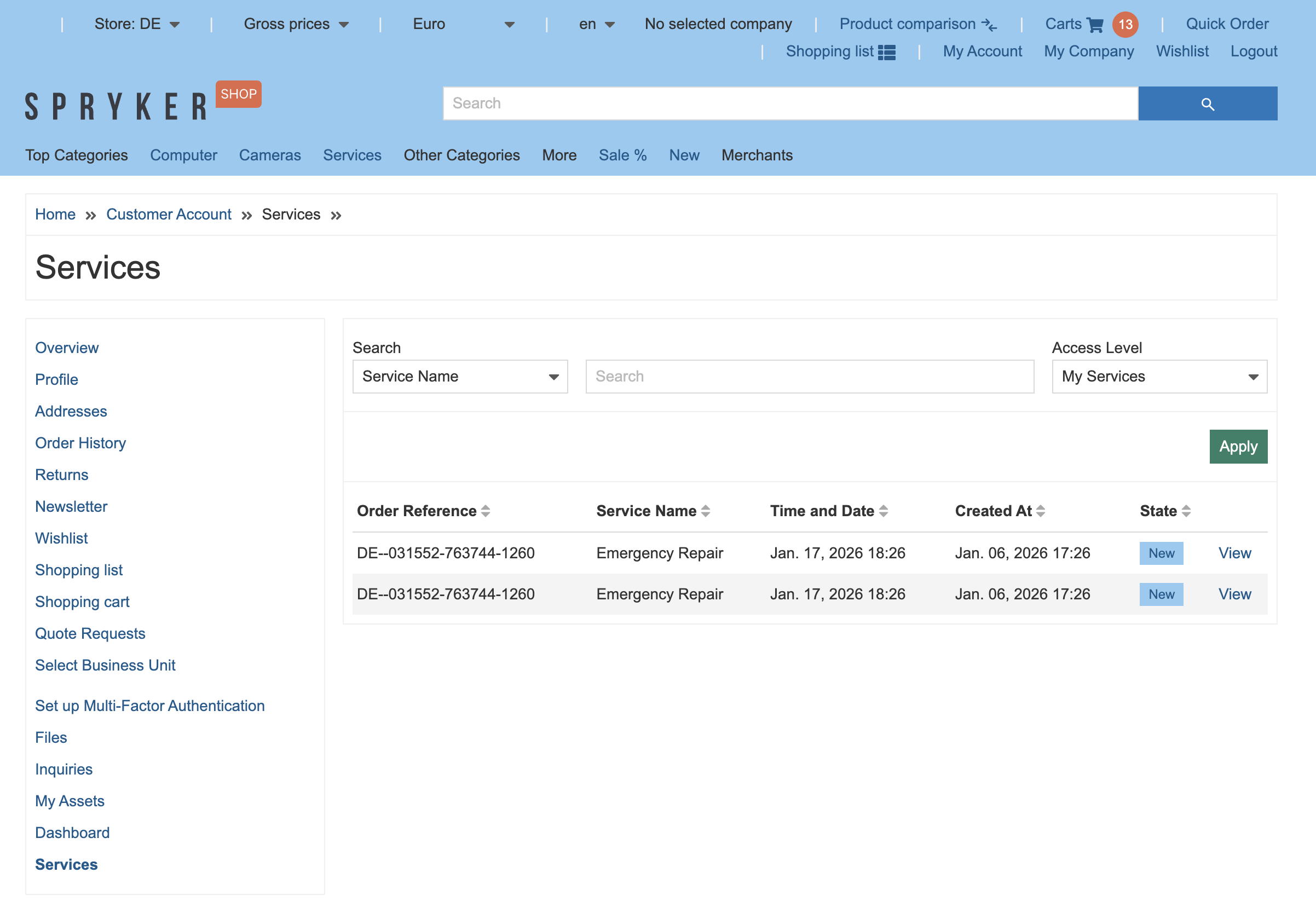
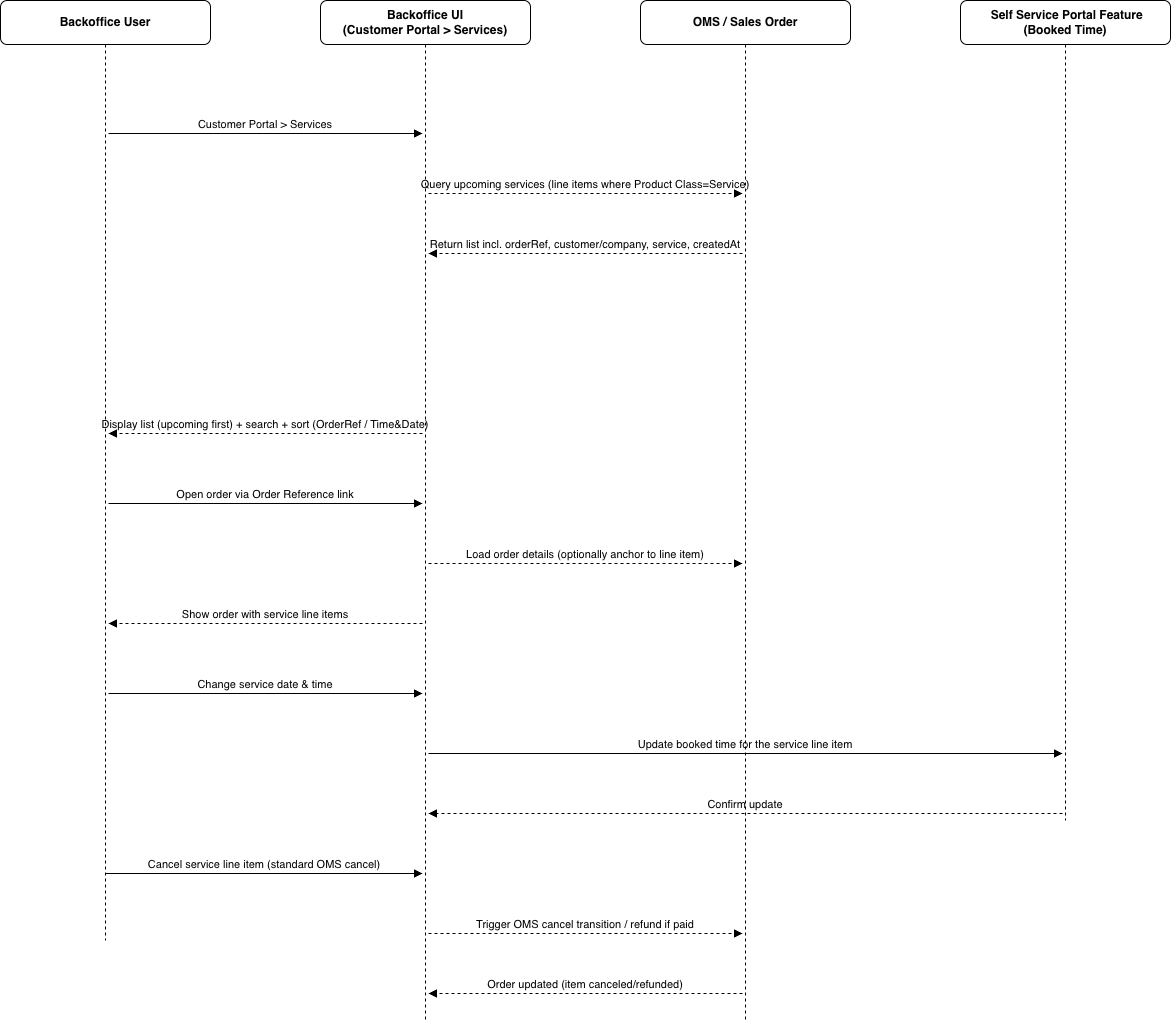
Customers can review purchased services in Home > Customer Account > Services (including order reference, service details, date/time, and state).
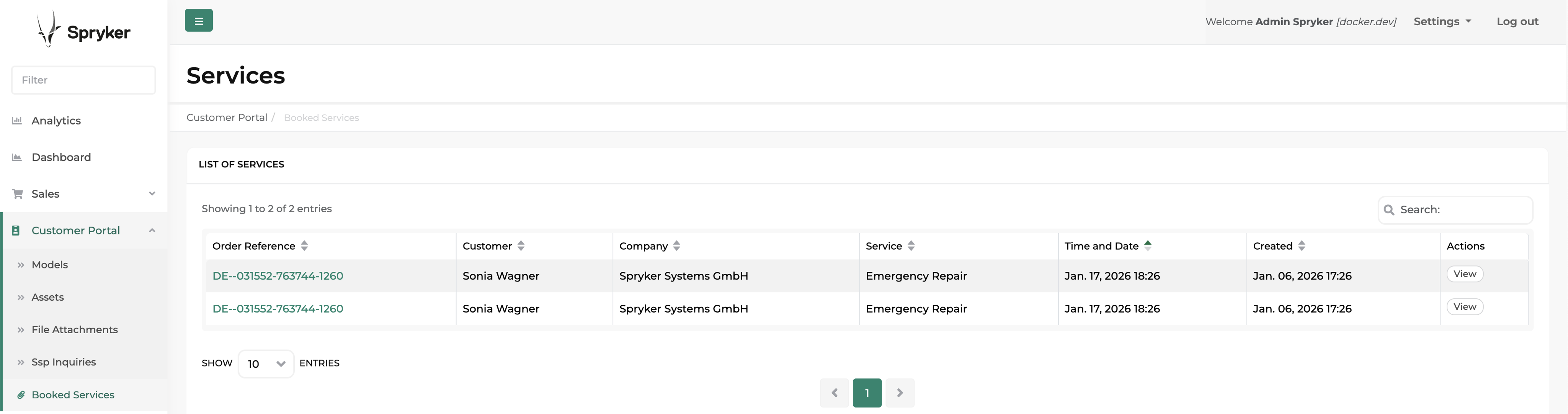
Back Office users can manage them under the Back Office > Customer Portal > Booked Services.
The checkout supports multi-step behavior by grouping On-Site Service items separately and allowing service point changes for those items (shipment type remains fixed). Current limitations include import-only offer pricing, reduced support for some B2B features on product offers, and no shipment type changes in cart or checkout.
Glossary
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| Click and Collect (C&C) | C&C business model refers to a retail strategy where customers make purchases online and then collect their ordered products from a physical store or a designated pickup location. This model combines the convenience of online shopping with the immediacy of in-store pickup. |
| Service Point | A service point is a physical location with a collection of services that are available within the service point. A service point can combine any kind of services to create any kind of service point like a warehouse or a physical store. What a service point actually is or can be considered to be is defined by the services it provides. |
| Service Point Address | Additional setting of Service Point that defines specific location of the service point where customers can go to collect their orders. It includes the street address, city, state, postal code and country. The service point address is provided to customers during the checkout process or in the order confirmation email, allowing them to know where to go for order pickup. |
| Opening Hours | Additional setting of Service Point that refers to the specific hours during which customers can access the location for order pickups or returns. These hours determine when the service point is operational and available for customer interactions. |
| Service Type | Different categories or classifications of services that a business offers to its customers. These service types are often determined by the nature of the business. Examples: Pickup service, Return service, Stock keeping service, etc. |
| Service | Service represents a specific service type that are provided (enabled) in specific Service point. A service is a capability within a service point that is offered to other entities, for example customers, merchants, third parties, basically any business entity. A service can be a point of sale, a locker where you can deliver to and customers can pick up their goods. It could be as well a loading point or loading dock. A service itself can be an aggregation of business entities that must be a logical part of this service. A service in this context is a point of interaction that exists in the real world. |
| Shipment Type | Method or option available for delivering products purchased by customers. It represents the different modes of shipment or delivery that can be chosen during the checkout process. The specific delivery types offered may vary depending on the e-commerce platform or the business’s logistics capabilities. Examples: Store pickup, Same-day delivery, Standard delivery, etc. |
| Product class | A product class is used to categorize a catalog item and drive service-specific behavior. For service products, it clearly distinguishes them from standard (physical) products and enables the required service flows in Back Office and Storefront. Out of the box, the main service-related product classes are: Service (identifies the product as a service sold via service offers linked to service points, services, and shipment types) and Scheduled (identifies the service as requiring date/time selection during checkout when appointment booking is mandatory). |
Feature models
Original feature model
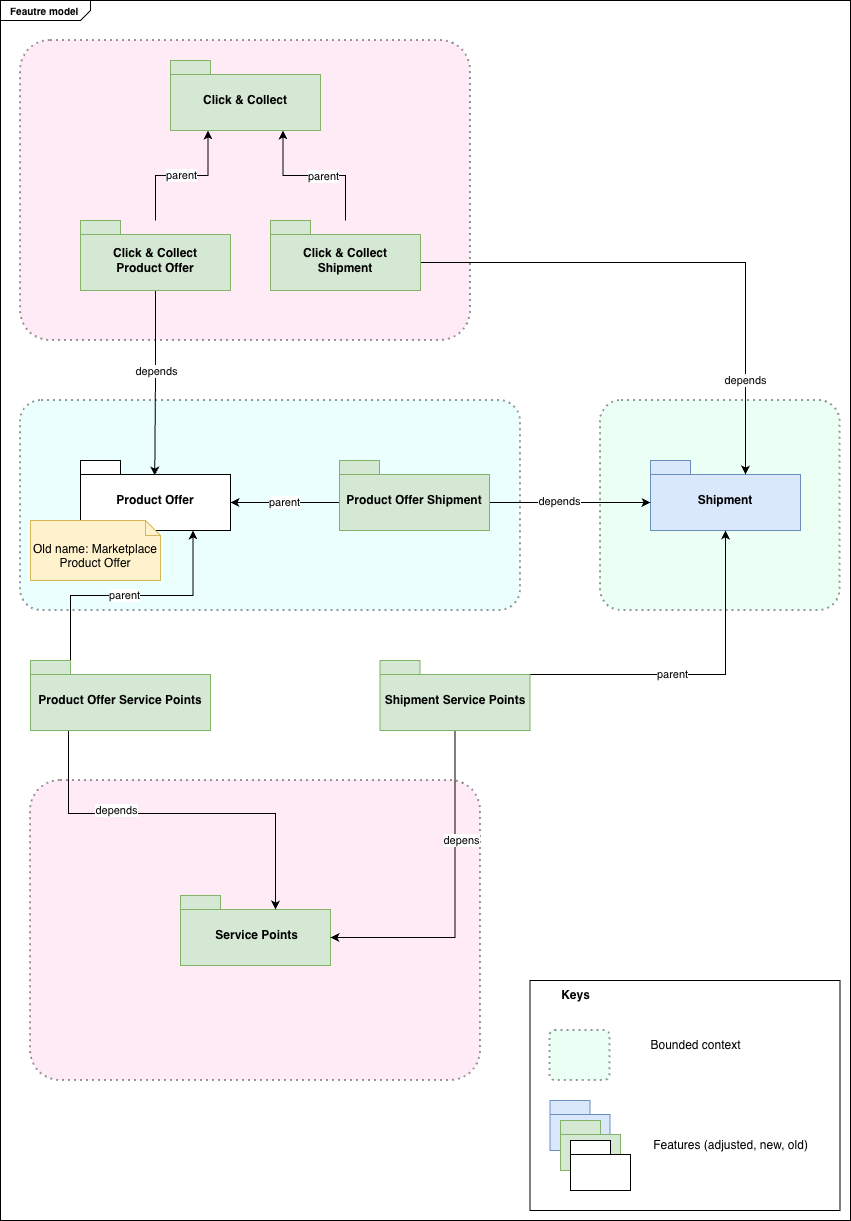
Self Service Portal feature model
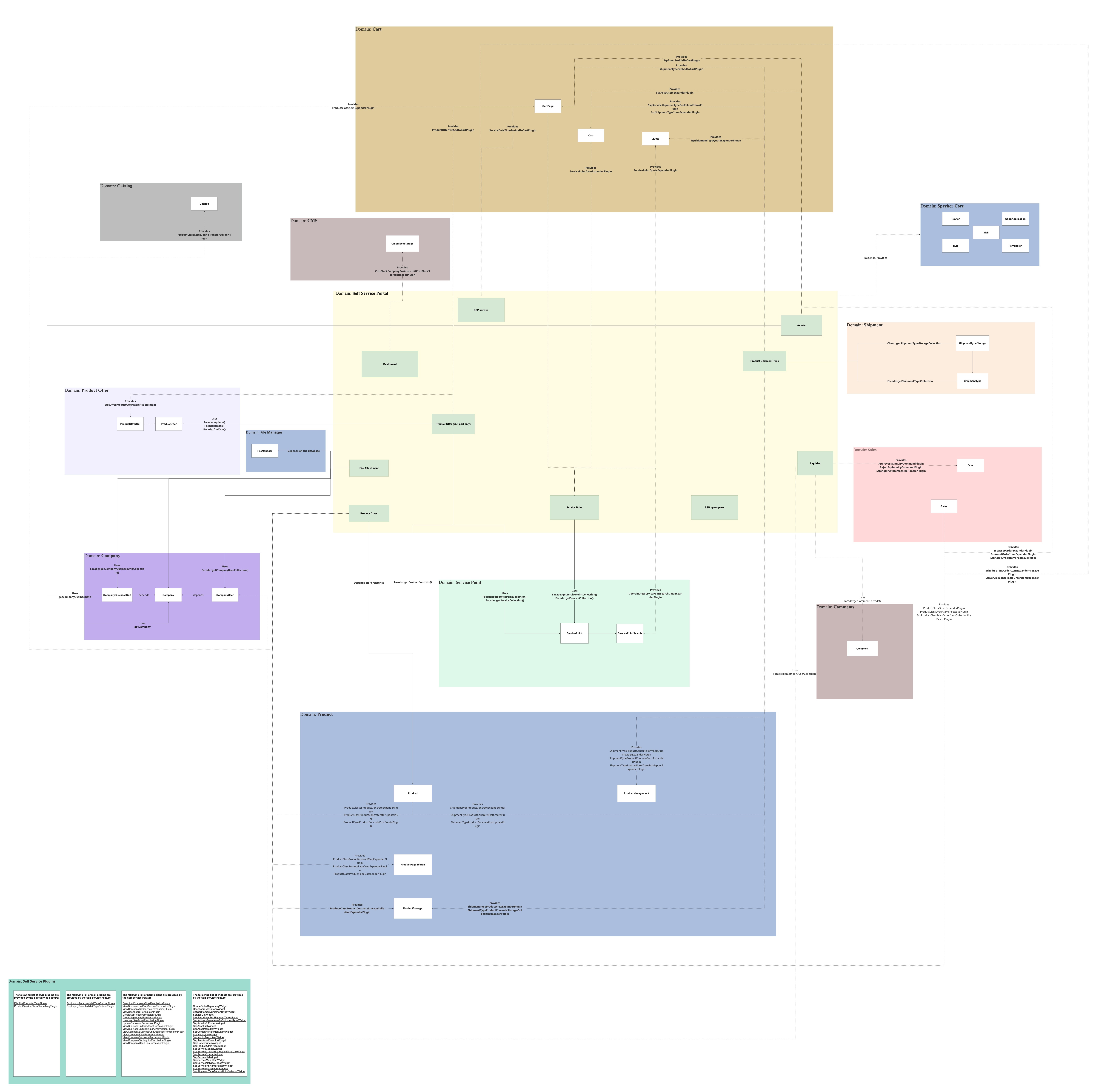
Domain model
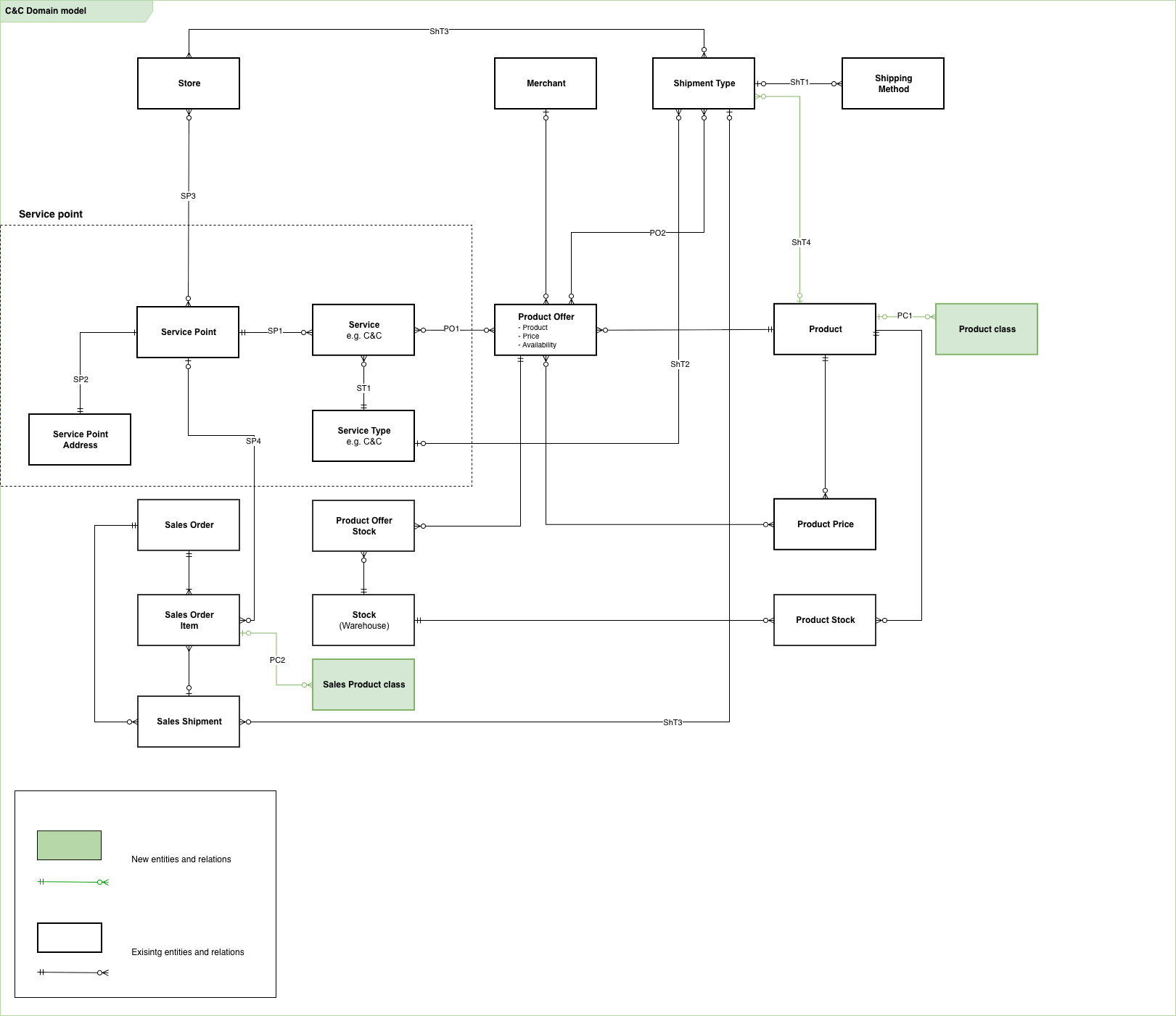
Entity connections
Service Point connections
| Connection | Description | Rationale |
|---|---|---|
| SP1 | Every service must belong to a service point. One service point can have many services. | Services are assigned to service points where it is provided, the service is an instance of its type that is available at this service point. |
| SP2 | A service point must have one address. | A service point represents a physical location in the real world, for that reason, it must have an address and geo-location. |
| SP3 | A service point can belong to one or many stores. | Service point can belong to one or many (Spryker) stores. Connection between service point and store enables possibility to provide services for specified online store. For example, if service point is connected to two online stores (Adidas and Reebok) it means that it could provide pickup service for orders created in these two stores as physical location where customers could collect their orders. |
Service Type connections
| Connection | Description | Rationale |
|---|---|---|
| ST1 | Service type can have many services enabled in specific service points. | Service that have same service type could be created for any number of service points. The service point could have only one service of specific type. |
Shipment Type connections
| Connection | Description | Rationale |
|---|---|---|
| ShT1 | Shipment type should have one or more delivery (shipping) methods. | Shipment type is a logical grouping of specific shipping methods. For example, “In store pickup” shipment type could be represented by following shipment methods: In-Store Counter pickup, Curbside pickup, Locker pickup, etc. |
| ShT2 | Shipment type can have none or one connected service type. | If shipment type that has connection with the service is selected on checkout, it means that user can select specific service point as a destination of corresponding shipment group. |
| ShT3 | A Shipment type can belong to one or many stores. | This connection makes shipment type available at specific stores. |
| ShT4 | A product can be distributed by multiple shipment types. | Enables flexible fulfillment options for the same product. |
Product Offer connections
| Connection | Description | Rationale |
|---|---|---|
| PO1 | Product offer can be connected to none or many services. | As Product Offer is used to share stock between various services (especially selling services). As stock physically can be only in one physical place, it means that Product offer MUST be connected to services that have same service point only. |
| PO2 | Product offer can be connected to none or many shipment types. | Same product offer could be connected with few shipment types. It means that offer could be delivered by two different shipment types but price of the product is same for both of them and stock is shared. So delivery will be done from one place. For example, single product offer can be created for Pickup and Ship from store shipment types. |
Product class connections
| Connection | Description | Rationale |
|---|---|---|
| PC1 | A product can be assigned to zero, one, or multiple product classes. | Supports flexible classification (for example, distinguishing Service vs. Scheduled services) without creating separate product structures. Enables feature logic and UI behavior based on product type. |
| PC2 | A sales order item stores a snapshot (copy) of the product classes that were assigned to the product at the time of purchase. | Preserves the purchase context for auditing and consistent processing even if product classes change later. Ensures correct downstream behavior (for example, service handling, scheduling, reporting). |
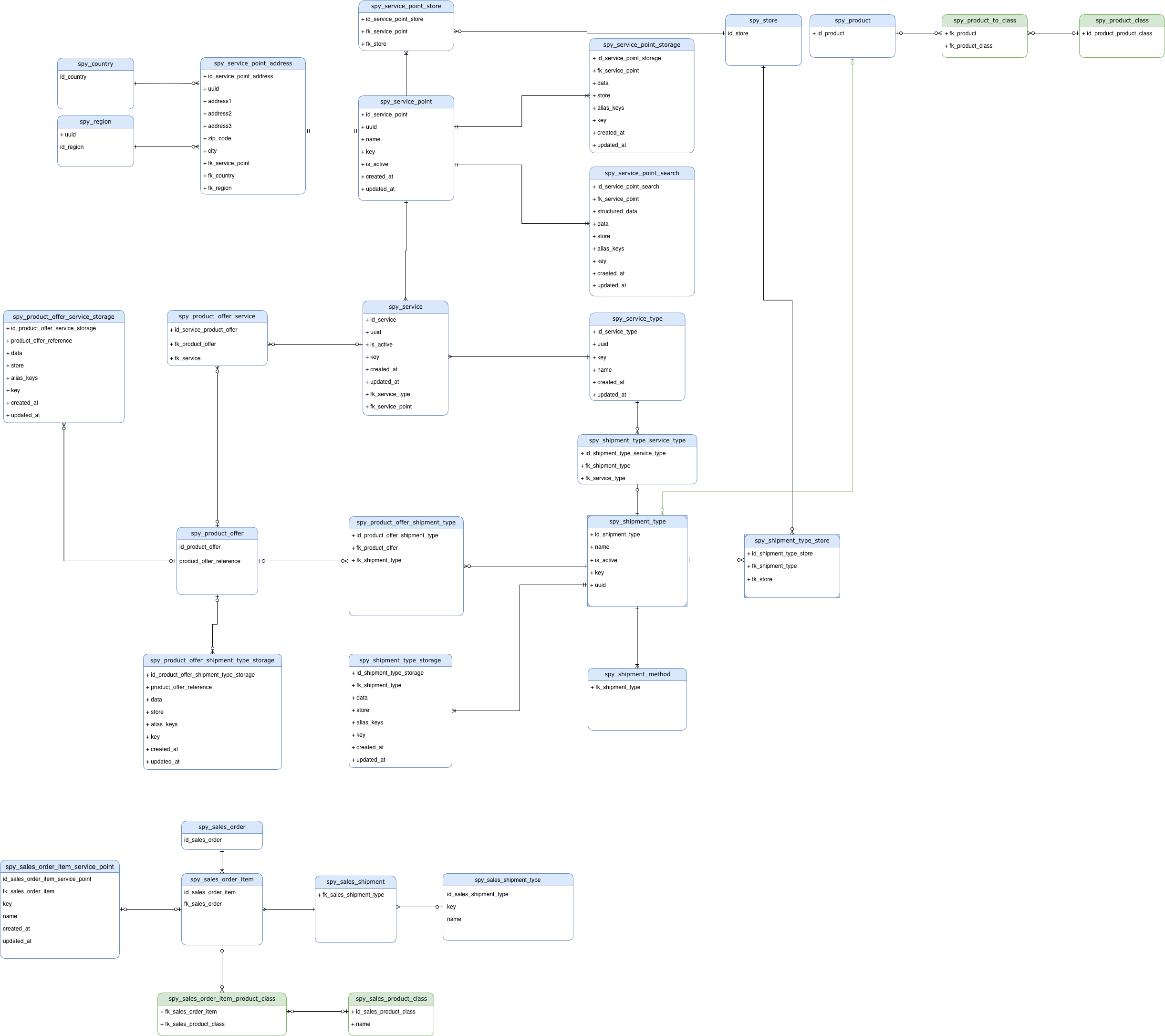
ERD diagram
Sequence diagrams
Back Office – Create Service Offer
Storefront – Buy Service Product
Back Office – Review Booked Services
Related documents
| Feature overviews |
|---|
| Self-Service Portal Service Management feature overview |
| Service Points feature overview |
| Shipment feature overview |
Thank you!
For submitting the form
