Dynamic Multistore
Edit on GitHubDynamic Multistore (DMS) lets you create and manage multiple stores within the same region in the Back Office. It streamlines the setup and maintenance of distinct stores tailored to various customer segments, regions, or product categories.
In the Back Office, in the Administration > Stores, you can view the list of stores in the current region. The Stores page shows all the stores within a specific region.

Creating a store
You can create a new store in the Back Office.

Assigning locales
When creating a store, you can assign locales and specify a default one for the store. This is useful for making the store accessible and user-friendly for different regions.

Adding currencies
To define which currencies the customers can you use, you can assign them to the store.

Store settings
To define additional store settings in the Settings tab. When creating a store, you can assign timezone per application or specify a default one.
Publishing and synchronizing
When the new queue infrastructure is published, the store becomes visible on the Storefront.
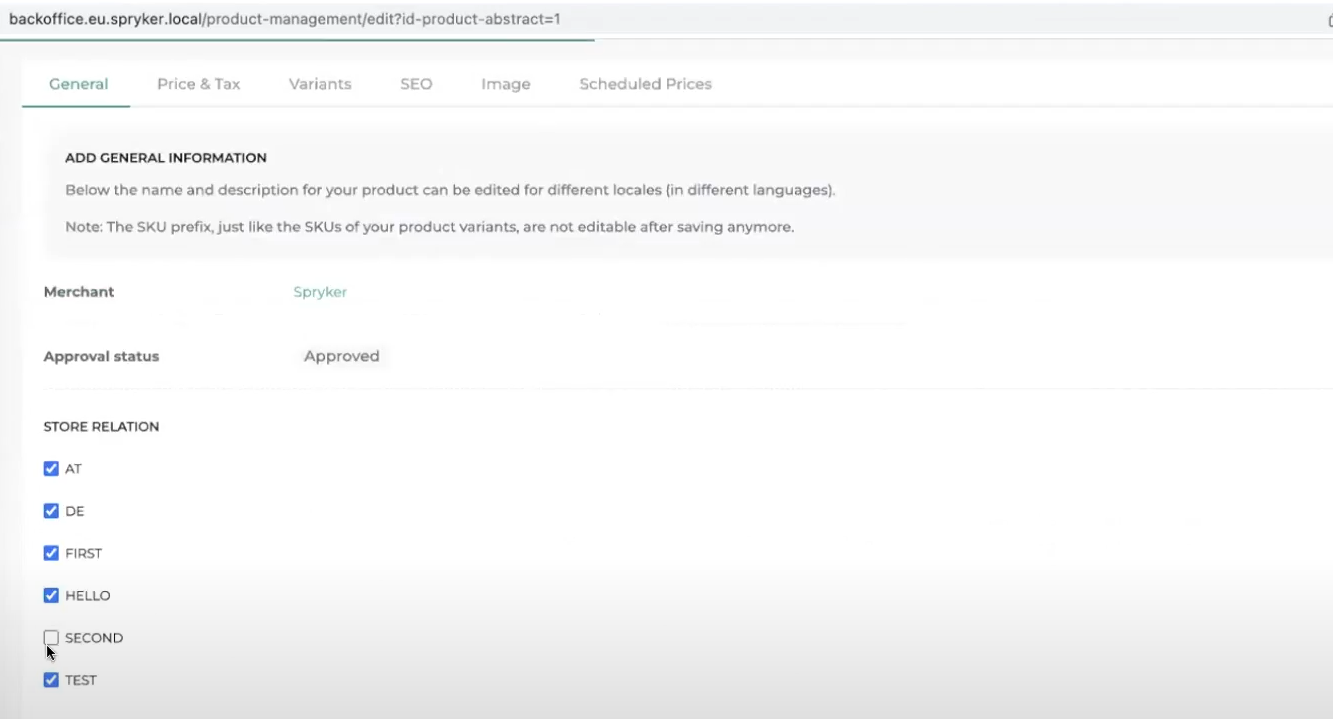
Assigning products and prices to stores
You can assign products and their prices to stores using the Back Office or other methods of creating products.
The following image shows how you can assign a product to a store.
The following image shows how you can assign a product price to a store.

Viewing stores on the Storefront
The following example shows the store created in the Back Office being available on the Storefront.

The product that was assigned to the store in Assigning products and prices to stores is available in this store.


Assigning CMS pages
By assigning CMS pages to stores, you can define which stores they are shown in.

When such a CMS page is published, it’s only visible in the store it’s assigned to.

Using the Storefront APIs
Normal storefront APIs can be used to fetch data from stores using the Store HTTP header, allowing access to Catalog Search or product details.
The following image shows the ability to call API endpoints with the exemplary “SECOND” store selected in the API call itself.

Adding stores using data import
You can add a new store using data import or in the Back Office. Adding a store in the Back Office is easier and faster, but you have to add each store across all environments.
Using data import, you can configure a new store once and deploy it across all environments. For instructions on importing stores, see Import data.
When you add a new store, to enable store-related entities for customers, you need to assign them to the store. Some of the store related entities:
- Products
- Categories
- CMS entities
- Prices
To avoid manually assigning entities in the Back Office, you can assign them using data import. For more details, see Import stores.
Differences in modes
This section describes the differences in different parts of application in DMS on and off modes.
Differences between applications with and without Dynamic Multistore
In this example, EU region has DE and AT stores. US region has a US store. Dynamic Multistore introduces the following changes in this setup:
-
URLs for Storefront, Back Office, Merchant Portal, and Glue API contain region instead of store name. For example–the URL of the Back Office is
https://backoffice.eu.mysprykershop.cominstead ofhttps://backoffice.de.mysprykershop.com. -
RabbitMQ virtual hosts contain region instead of store. For example–
eu-dockerinstead ofde-docker.


- Jenkins job names contain region instead of store. For example–
EU_queue-worker-startinstead ofDE_queue-worker-start.


- Elasticsearch indexes contain store as a part of the index name for Dynamic Multistore enabled and disabled modes.


-
Redis keys contain store as a part of the key name for Dynamic Multistore enabled and disabled modes.
-
When Dynamic Multistore is enabled, customers can switch between available stores for a region. When a customer changes a store, it’s set to the
_storequery parameter. Using the query parameter, the store is added to session under thecurrent_storekey. It’s used for fetching store-related data.

Store context in different applications with Dynamic Multistore
All the applications work with the several stores within one region with the following differences:
- Back Office and Merchant Portal operate with data from all the stores within a region and don’t require a store context.
- Storefront, GlueStorefront, and Glue require a store context and operate within only one provided store. If a store isn’t provided, the default one is used.
Cloud infrastructure differences
DMS doesn’t affect cloud infrastructure. The only related changes are in the deployment files, which are described in the following sections.
Deployment file differences
Applacation configurations are defined differently depending on whether DMS is on or off.
Environment variables configuration
DMS off:
SPRYKER_HOOK_BEFORE_DEPLOY: 'vendor/bin/install -r pre-deploy.dynamic-store-off -vvv'
SPRYKER_HOOK_AFTER_DEPLOY: 'true'
SPRYKER_HOOK_INSTALL: 'vendor/bin/install -r production.dynamic-store-off --no-ansi -vvv'
SPRYKER_HOOK_DESTRUCTIVE_INSTALL: 'vendor/bin/install -r destructive.dynamic-store-off --no-ansi -vvv'
SPRYKER_YVES_HOST_DE: de.
SPRYKER_YVES_HOST_AT: at.
DMS on:
SPRYKER_HOOK_BEFORE_DEPLOY: 'vendor/bin/install -r pre-deploy -vvv'
SPRYKER_HOOK_AFTER_DEPLOY: 'true'
SPRYKER_HOOK_INSTALL: 'vendor/bin/install -r dynamic-store --no-ansi -vvv'
SPRYKER_HOOK_DESTRUCTIVE_INSTALL: 'vendor/bin/install -r destructive --no-ansi -vvv'
SPRYKER_DYNAMIC_STORE_MODE: true
SPRYKER_YVES_HOST_EU: yves.eu.
Regions configuration
DMS off:
regions:
stores:
DE:
services:
broker:
namespace: de_queue
key_value_store:
namespace: 1
search:
namespace: de_search
session:
namespace: 2
AT:
services:
broker:
namespace: at_queue
key_value_store:
namespace: 3
search:
namespace: at_search
session:
namespace: 4
DMS on:
regions:
broker:
namespace: eu-docker
key_value_store:
namespace: 1
search:
namespace: eu_search
Applications configuration
The following examples show the difference for the merchant-portal application. The difference is similar for all the applications.
DMS off:
mportal:
application: merchant-portal
endpoints:
mp.de.:
entry-point: MerchantPortal
store: DE
primal: true
services:
session:
namespace: 7
mp.at.:
entry-point: MerchantPortal
store: AT
services:
session:
namespace: 8
DMS on:
mportal:
application: merchant-portal
endpoints:
mp.eu.:
region: EU
<<: *frontend-auth
entry-point: MerchantPortal
primal: true
services:
session:
namespace: 7
The domain structure in DMS on mode enables store switching within the same domain.
Differences in the execution of console commands
With DMS off, store-aware console commands are executed with the APPLICATION_STORE environment variable. Example:
APPLICATION_STORE=DE console search:setup:sources
With DMS on, all the store-aware console commands are executed with the --store parameter. Example:
console search:setup:sources --store=DE
If a store isn’t provided as a parameter, the command is executed for all stores within a current region.
Rules for implementing custom console commands in environments with Dynamic Multistore
Store(Facade|Client)::getCurrentStore()must not be used in the code the console command executes.- All store-aware commands must implement
Spryker\Zed\Kernel\Communication\Console\StoreAwareConsoleand execute actions for a specific store if the store parameter is provided; if not provided, actions are executed for all the stores in the region. - We recommend using the
--storeparameter instead ofAPPLICATION_STOREenv variable; both methods are supported.
Store-specific entities in Data Exchange API
There’re no specific requirements, and the changes you need to make depend on the database structure. These entities should be handled in the same way as any other exposed through Data Exchange API database table.
Data import performance
The number of stores affects data import speed: the more stores you have, the slower the data import. Importing products for 40 stores takes approximately 5 times longer than for 8 stores.
Limitations
With Dynamic Multistore, the separated setup is only possible with stores belonging to different regions. To learn about setups, see Multi-store setups.
Thank you!
For submitting the form
