Inherited scope
Edit on GitHubInherited scope rules apply when you need to grant access to an entity (child) that inherits from another entity (parent). Here are a few examples of inheritance:
- MerchantProductAbstracts → Merchants (through
MerchantProductAbstract.fk_merchant) - MerchantSalesOrders → Merchants (through
MerchantSalesOrder.merchant_reference) - Shipments → Orders (through
Shipment.order_reference)
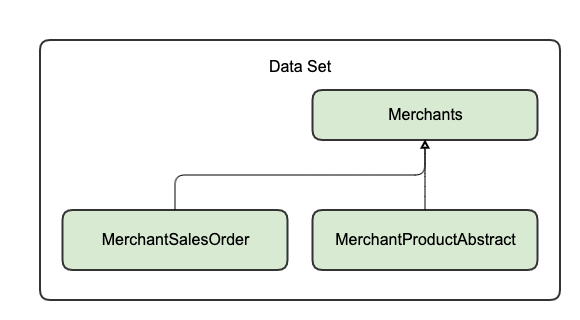
Inheritance rules (child-parent relationship) are set in the configuration. For more details, see Persistence ACL configuration.
Inherited scope functionality has one unique feature: it’s sufficient to have read access to the parent for successful inheritance for any operation (create/read/update/delete).
Here is an example where a user has a configuration where SpyMerchantProductAbstract inherits from SpyMerchant, and the user has 2 rules:
- inherited for
MerchantProductAbstract - segment for
Merchant
spy_acl_entity_rule
| fk_acl_entity_segment | fk_acl_role | entity | permission_mask | scope |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| null | 15 | Orm\Zed\MerchantProduct\Persistence\SpyMerchantProductAbstract |
AclEntityConstants::OPERATION_MASK_READ |
AclEntityConstants::SCOPE_INHERITED |
| 5 | 15 | Orm\Zed\Merchant\Persistence\SpyMerchant |
1 | 1 |
spy_acl_entity_segment
| id_acl_entity_segment | name | reference |
|---|---|---|
| 5 | Merchant Video King | merchant-video-king |
spy_acl_entity_segment_merchant
| fk_merchant | fk_acl_entity_segment |
|---|---|
| 112 | 5 |
Query before the Persistence ACL:
SELECT * FROM `spy_merchant_product_abstract` ORDER BY `updated_at` DESC;
Query after the Persistence ACL:
SELECT `spy_merchant_product_abstract`.*
FROM `spy_merchant_product_abstract`
INNER JOIN `spy_merchant` ON (`spy_merchant_product_abstract`.`fk_merchant` = `spy_merchant`.`id_merchant`)
INNER JOIN `spy_acl_entity_segment_merchant`
ON (`spy_merchant`.`id_merchant` = `spy_acl_entity_segment_merchant`.`fk_merchant`
AND `spy_acl_entity_segment_merchant`.`fk_acl_entity_segment` IN (5))
ORDER BY `spy_merchant_product_abstract`.`updated_at` DESC;
It is important to understand that the permissions are checked in the context of roles. Rules of one role do not affect the rules of another. For details, see Execution Flow. Below is an example of the two roles:
- DE product manager (Full CRUD for products in the DE store)
- US product viewer (View only for products in the US store)
spy_acl_role
| id_acl_role | name | reference |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | DE product manager | de_product_manager |
| 2 | US product viewer | us_product_viewer |
spy_acl_entity_rule
| id_acl_entity_rule | fk_acl_entity_segment | fk_acl_role | entity | permission_mask | scope |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | null | 1 | Orm\Zed\Product\Persistence\SpyProduct |
15 | 2 |
| 2 | null | 1 | Orm\Zed\Product\Persistence\SpyProductAbstract |
15 | 2 |
| 3 | null | 1 | Orm\Zed\Product\Persistence\SpyProductAbstractStore |
15 | 2 |
| 4 | 1 | 1 | Orm\Zed\Store\Persistence\SpyStore |
1 | 1 |
| 5 | null | 2 | Orm\Zed\Product\Persistence\SpyProduct |
1 | 2 |
| 6 | null | 2 | Orm\Zed\Product\Persistence\SpyProductAbstract |
1 | 2 |
| 7 | null | 2 | Orm\Zed\Product\Persistence\SpyProductAbstractStore |
1 | 2 |
| 8 | 2 | 2 | Orm\Zed\Store\Persistence\SpyStore |
1 | 1 |
Rules with IDs 1, 2, 3 and 4 refer to one role (fk_acl_role: 1), and rules with IDs 5, 6, 7 and 8 to another (fk_acl_role: 2). When a user has both roles and performs Update on a Product, the Persistence ACL engine will perform the following:
- it will only find role
1(since it has a rule for updating a product). - the role
2will not be considered at all since it does not allow products to be updated.
The context of a rule is determined by the role to which it’s attached. Because of this, a user with such a set of roles and rules will be able to:
- perform CRUD actions for products in the DE store.
- have read-only permissions for products in the US store.
Thank you!
For submitting the form
