Manage stocks in a multi-store environment: Best practices
Edit on GitHubIn a multi-store environment, you can manage relationships between warehouses, stores, and databases in several ways. This article contains scenarios that can help you choose the most suitable warehouse management workflow and implement it using the Inventory Management feature.
Scenario 1: Separate warehouses and databases
To enable this scenario for your project, a developer needs to configure it.
Suppose you own a large e-commerce business and ship orders worldwide. You want to manage logistics and products effectively. You also want each store to be completely independent from each other, so user, product, and other data is not shared between stores.
In this case, each store can have its own warehouse and a separate database. Stocks, product reservations, and availability are not co-dependent between stores, and therefore do not need to be synced:
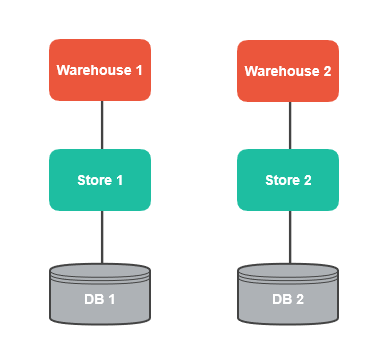
This scenario is appropriate for big businesses managed from various locations, with worldwide deliveries. These stores do not depend on each other in any way and do not require additional communication or synchronization.
Scenario 2: A shared warehouse but separate databases
To enable this scenario for your project, a developer should configure it. See implementation reference for recommendations.
Suppose you have a large e-commerce business, with many products and orders, and you want to separate all data for each of your stores. For some reason you do not need multiple warehouses, either because they cannot be spread out across different locations or your deliveries are within a specific part of the world.
In this case, you can have a common warehouse for all your stores but separate databases. Since the warehouse is shared, for the correct product availability calculations, product reservations must be synced between the databases:
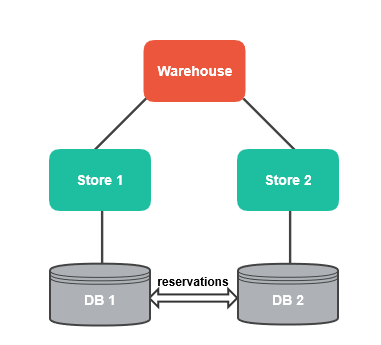
This approach is appropriate for big businesses that can’t have or don’t need multiple warehouses, but still wish to have the data of each store separated.
Implementation reference
To implement this scenario, you need these three additional database tables:
spy_oms_product_reservation_storeto store reservation requests from other stores.spy_oms_reservation_change_versionto store information about the time when the last reservation occurred.spy_oms_reservation_last_exported_versionto store historic information on the last time reservaions were exported to other stores.
Also, there are plugins to help you implement synchronization of the reservations:
| PLUGIN | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
| /Spryker/Zed/Oms/Business/OmsFacadeInterface::importReservation | You can use this plugin when reading export data from another store. The plugin stores reservation information to spy_oms_product_reservation_store table and updates all timestamps accordingly. |
| /Spryker/Zed/Oms/Communication/Plugin/Oms/ReservationHandler/ReservationVersionHandlerPlugin | The plugin is called when a customer makes an order, and a reservation is made. It stores reservation in the spy_oms_reservation_change_version database table. Register this plugin in /Pyz/Zed/Oms/OmsDependencyProvider::getReservationHandlerPlugins plugin stack. |
| /Spryker/Zed/Oms/Communication/Plugin/Oms/ReservationImport/ReservationExportPlugin | The plugin is called when a reservation export to another store is initiated. This plugin decides whether the export must be accepted. We do not provide the delivery mechanism: you could do this with files or a queue. For example, when ReservationExportPlugin is called, you can write a file copy to another server and read it there. Same for queue: you could publish an event in the queue and then consume it on the other end. |
There is a console command to export all reservations: /Spryker/Zed/Oms/Communication/Console/ExportReservationConsole. It triggers ReservationExportPlugin with reservations amounts to export. You can run this command as a cronjob.
Scenario 3: Separate warehouses but a shared database
This is the default scenario implemented in the Spryker Demo Shops.
Suppose you own a medium to large e-commerce business and ship orders worldwide. You want to manage logistics and products effectively, so each store has its own warehouse. You also want product reservations and availability to be separated per store, but you want all the data stored in one place. For example, if a product is unavailable in the DE store, but available in the AT store, a registered user can simply switch from the DE store to AT store and buy the product there.
In this case, consider separated warehouses but a shared database:
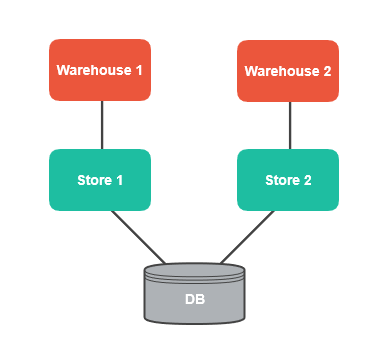
When a buyer places an order, a reservation record is created in the database. The record also contains information about the store the reservation is made for.
This scenario is good for medium and large online shops that want to have a common database of product, user, and other data. It’s a good option to, for example, allow registered users to buy from any store without having to re-register.
Scenario 4: Warehouse and database are shared between stores
To enable this scenario for your project, a developer needs to configure it.
Suppose you own a small or large e-commerce business and can’t have or don’t need separate warehouses per store. You also want all the data stored in one place. So, for example, if a product is unavailable in the DE store, but available in the AT store, a registered user can switch from the DE store to AT store and buy the product there.
In this instance, consider having a shared warehouse and a shared database for all stores. Since the warehouse is shared, for the correct product availability calculations, product reservations are synced between the stores:
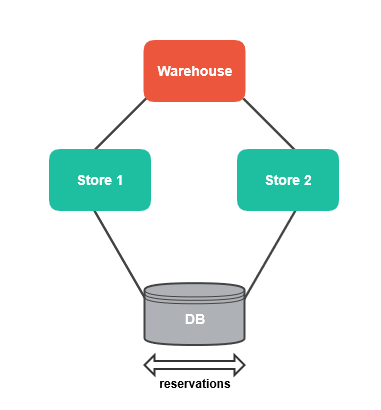
When a buyer places an order in one of the stores, the reservation with the store identifier is stored in the database. An event is created and published in the queue, and synchronization with the other stores happens.
This scenario is especially good for small online shops with one warehouse that want to have a common database of product, user, and other data.
Thank you!
For submitting the form
